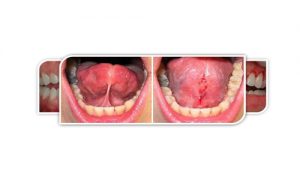
Laser surgery is a type of surgery that uses a laser (in contrast to using a scalpel) to cut tissue. Examples include the use of a laser scalpel in otherwise conventional surgery, and soft-tissue laser surgery, in which the laser beam vaporizes soft tissue with high water content.
Laser Dentistry: What is Laser Dentistry?
What is laser dentistry? If you’ve never heard of this innovative type of dental care, now is the time to learn. Laser dentistry is a minimally invasive option when you’re facing gum surgery, cavity treatment, or other oral issues. Discuss your laser surgery options with one of our dentists today.
Laser Dentistry: An Overview Medical professionals use lasers, which are extremely focused light beams, to alter or remove tissue in small amounts. Laser surgery is not limited to dentistry, but many people have never heard of laser dentistry before having it done. Dentists use lasers in a variety of procedures involving the inside of the mouth, be it to remove overgrown tissue, to reshape the gums, or to whiten teeth.
Sometimes, laser dentistry is ideal for children who become anxious or afraid when having dental work done.
Soft tissue lasers
Soft-tissue laser surgery is used in a variety of applications in human (general surgery, neurosurgery, ENT, dentistry, orthodontics,and oral and maxillofacial surgery as well as veterinary surgical fields.
Soft Tissue Lasers
The soft tissue lasers use a light wavelength that hemoglobin and water absorb easily. Hemoglobin is the molecule found in blood, which makes soft tissue lasers ideal for gum work. Some soft tissue lasers are diode lasers, which is a type of continuous-wave laser.
These lasers are ideal for cutting into soft tissue and sealing the exposed blood vessels at the same time. This is the reason you don’t bleed very much during laser dentistry and why healing is quicker after laser dentistry. Soft tissue lasers are great for cosmetic procedures because you can begin to
see results right away. Soft tissue lasers are used for:
Lengthening crowns.
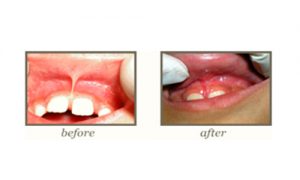
Dealing with restricted tongue movement.
Reshaping the gums to create a more pleasing smile.
Removing folds in oral soft