Dental prosthetics
Dental prosthetics are the branch of dentistry that deals with the reconstruction of damaged teeth or the replacement of missing teeth.
What is a fixed dental prosthesis (fixed denture)?
A fixed prosthesis consists of the artificial reconstitution of the crown of a damaged or absent tooth as close as possible to its natural state. Individual crowns can be supported by a natural, living, or devitalized root, as well as by a dental implant. The preparation of a natural tooth for a crown requires an important reduction of the coronal part of the tooth. This invasive act, lacking in the preservation of dental tissue, is only practiced today in situations of last recourse as the new adhesive cementing techniques allow a much more conservative approach. The replacement of a tooth by a dental implant and a crown represents one of the best solutions. The crown can either be cemented or screwed onto the implant.
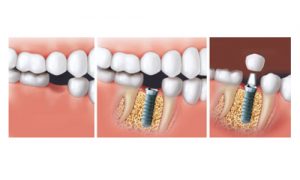
A bridge corresponds to the replacement by crowns of one or more missing teeth supported by abutment crowns (“pillars”) adjacent to the gaps. Today, abutment crowns are generally supported on dental implants. Bridges on natural teeth have become increasingly rare as they necessitate an
invasive preparation of the adjacent teeth and, in the case of problems, are difficult to repair.
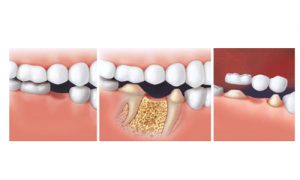
Crowns are composed generally of two elements:
A framework (“cap”): ensures the mechanical resistance of the prosthetic work and is usually made of precious metal alloys (gold), titanium, or high performance ceramic, such as zirconium, thus offering the possibility of highly aesthetic, metal-free restoration. Cosmetic ceramic: allows an aesthetic prosthetic work and is consists of a ceramic base.
New high-tech, ceramic technologies using lithium disilicate (E-max Ivoclar) offer wide-ranging possibilities, allowing restorations without framework, both highly aesethetic and resistant.
What is a removable denture?
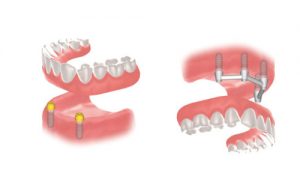
A removable dental prosthesis, commonly called dentures, is a prosthesis that can be taken out. It can be partial for the replacement of one or several teeth or a complete set of teeth. The partial removable denture, when it is not a temporary solution entirely made of resin, has a metallic base (cobalt-chrome, sometimes also titanium or a precious alloy), which lies on the remaining teeth carefully prepared for the integration of a clasp, and the mucosa. The metal is needed to make the clasps and support the prosthetic resin teeth. The complete removable dental denture is generally entirely made of resin and must lie on the oral mucosa as much as possible. The retention (fit) of a total upper prosthesis is much more favourable
than a lower prosthesis. Whether it be a partial or complete prosthesis, the retention can be improved spectacularly by fasteners (“snaps”) fixed on implants.